Different License types
There are 3 different types of licenses with corresponding dvds for Windows Server 2008 R2: Volume License, OEM and Timebased Evaluation. All these licenses have different time limits before you have to activate in order to continue using the Operating System. There is a possibility to reset the evaluation period for a few times which is called “rearming”. This method is also explained in the Microsoft Knowledge Base. The different licenses with corresponding DVD-image, hashes and evaluation times are as follows:Windows Server 2008 R2 Evaluation English (TIMEBASED_EVAL) – Usable: (10 days + 5 * 10 days using rearm) + 180 days after activating = 240 days
Filename: 7600.16385.090713-1255_x64fre_server_eval_en-us-GRMSXEVAL_EN_DVD.iso (download)
SHA1: 799BF8DA077A3E842AA97C990E468B3AA7BDA4EB
MD5: 134F607CF4C633EF11D2576D1C635D08
Windows Server 2008 R2 OEM English (RETAIL) – Usable without activation: 30 days + 3 * 30 days using rearm = 120 days
Filename: 7600.16385.090713-1255_x64fre_server_en-us_OEM-GRMSXFREO_EN_DVD.iso (only available for OEM manufacturers)
SHA1: 515A9E7F4C7DF41AACA6872CB806DABD15BF7D64
MD5: 4FFB420543F5A9265BE5EEDB6C4E55A2
Windows Server 2008 R2 VL English (VOLUME_KMSCLIENT) – Usable without activation: 30 days + 3 * 30 days using rearm = 120 days
Filename: 7600.16385.090713-1255_x64fre_server_en-us_VL-GRMSXVOL_EN_DVD.iso (only available for MSDN and TechNet subscribers)
SHA1: AD855EA913AAEC3F1D0E1833C1AEF7A0DE326B0A
MD5: 0207EF392C60EFDDA92071B0559CA0F9
As you can see you can use the evaluation version of Windows Server 2008 R2 for free for 6 months and even for more than 7 months if you use the rearm method described below!
Rearming
1. Check your remaining time by clicking Run in the Start menu and entering slmgr.vbs -dli. After clicking OK a window will show up which shows you the remaining time before expiration.2. If you have less than one day left rearm your license so you have 10 days left again. To do this click Run in the Start menu, enter slmgr.vbs -rearm and click OK. After a few moments a window will popup that shows you the rearm has been completed and you have to restart your system.
3. After restaring your system verify that the rearm has worked by running slmgr.vbs -dli again. The remaining time should now be reset to 10 days!
Checking rearm count left
You can rearm the Evaluation version of Windows Server 2008 R2 up to 5 times. To check how much rearms you have left click Run in the Start menu, enter slmgr.vbs -dlv and click OKActivating
1. After you used all rearms it’s time to activate. To activate click Activate Windows online now Windows Activation assistant.2. Wait until the online key verification and activation has finished.
3. If everything went right Windows will now be activated with a 180 days license and a watermark appears on your desktop.
Removing Desktop Watermark
1. Download watermark.zip (9KB) from win2008r2workstation.2. After downloading the zip extract the zip, run install.cmd as an Administrator and follow the instructions on the screen. After a successful installation, reboot your pc to remove the watermark. If you want to do this manually, open %SystemRoot%\System32\en-US\user32.dll.mui with a resource editor and replace the strings in the following resources with a space (” “): 45.715, 45.716, 46.* and 47.739.
If you get a sharing violation error during the installation, try running it again in Safe Mode. I Couldn’t test it myself because for some reason I can’t get into Safe Mode. Please confirm this works!
http://www.win2008r2workstation.com/win2008r2/240-days-evaluation
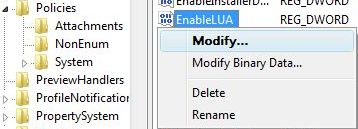
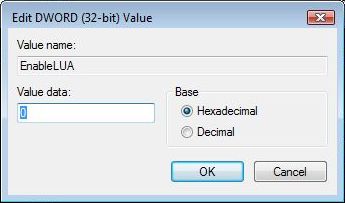
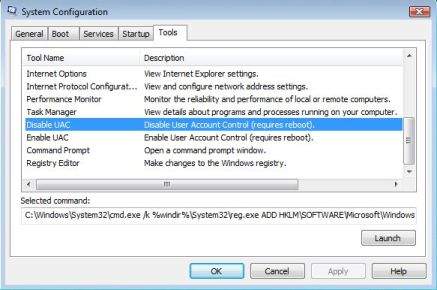
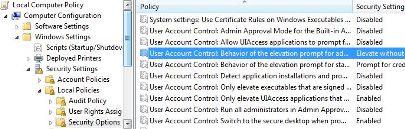
 Caution
Caution  Note
Note 

